https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.06049.pdf
Marios Savvides
Carnegie Mellon University and Michigan State University
We propose local binary convolution (LBC), an efficient alternative to convolutional layers in standard convolutional neural networks (CNN). The design principles of LBC are motivated by local binary patterns (LBP). The LBC layer comprises of a set of fixed sparse pre-defined binary convolutional filters that are not updated during the training process, a non-linear activation function and a set of learnable linear weights. The linear weights combine the activated filter responses to approximate the corresponding activated filter responses of a standard convolutional layer. The LBC layer affords significant parameter savings, 9x to 169x in the number of learnable parameters compared to a standard convolutional layer. Furthermore, the sparse and binary nature of the weights also results in up to 9x to 169x savings in model size compared to a standard convolutional layer. We demonstrate both theoretically and experimentally that our local binary convolution layer is a good approximation of a standard convolutional layer. Empirically, CNNs with LBC layers, called local binary convolutional neural networks (LBCNN), achieves performance parity with regular CNNs on a range of visual datasets (MNIST, SVHN, CIFAR-10, and ImageNet) while enjoying significant computational savings.
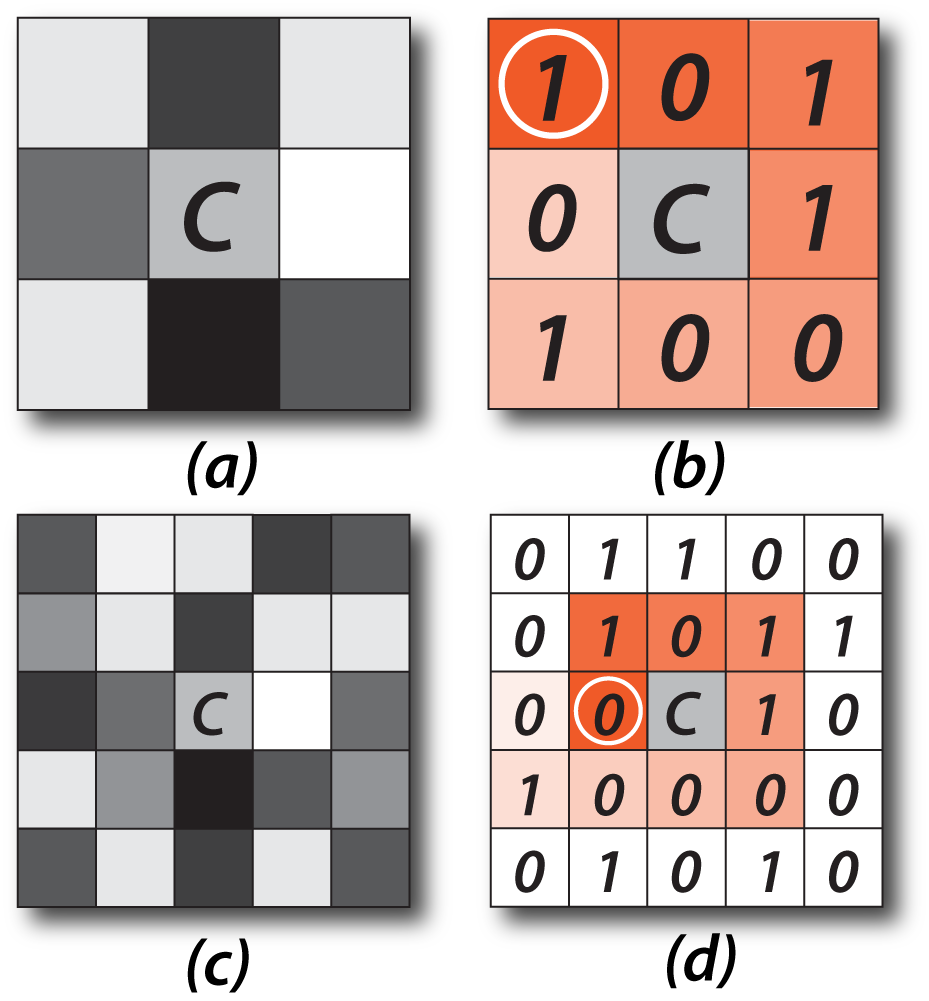
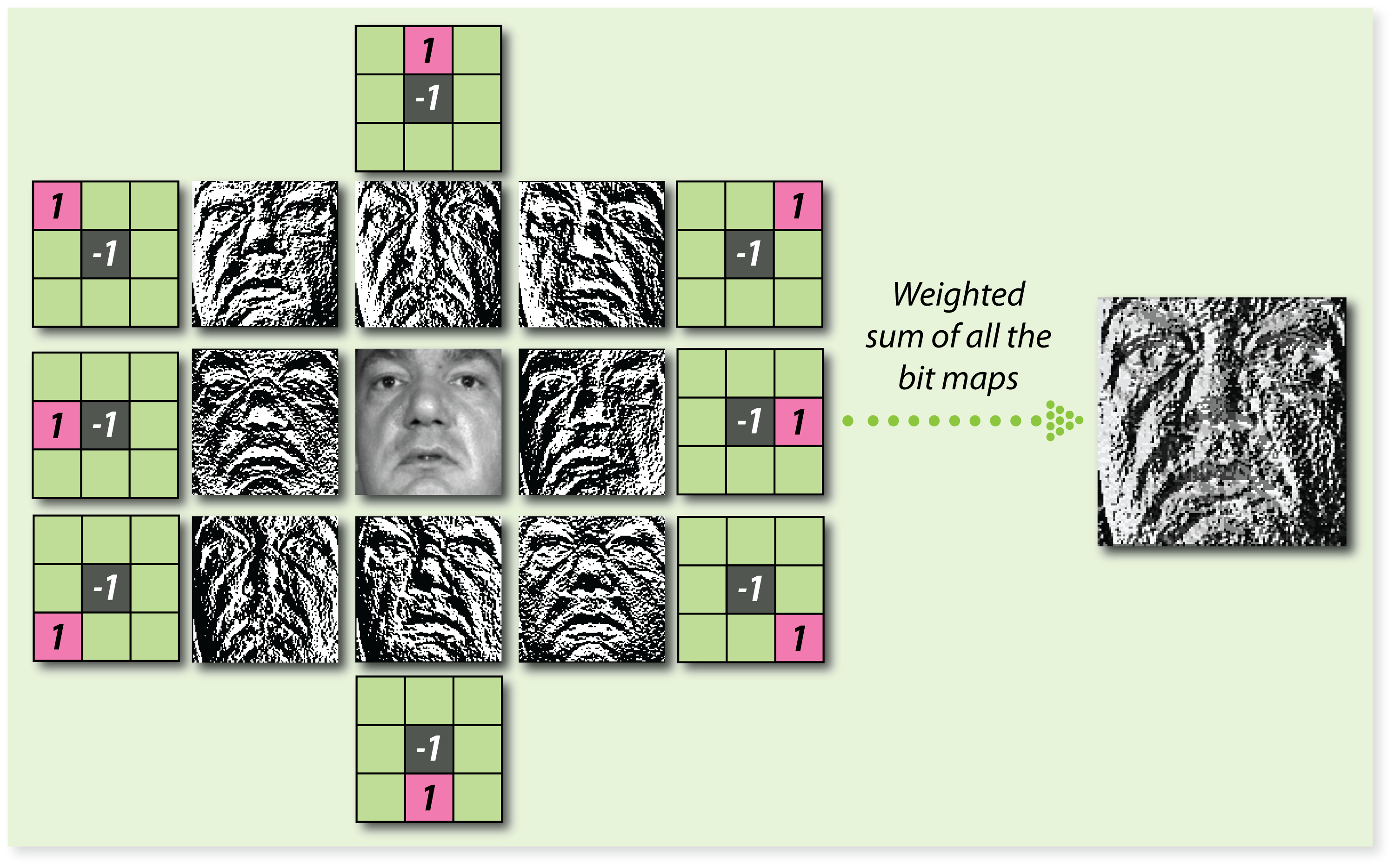
We draw inspiration from local binary patterns that have been very successfully used for facial analysis.
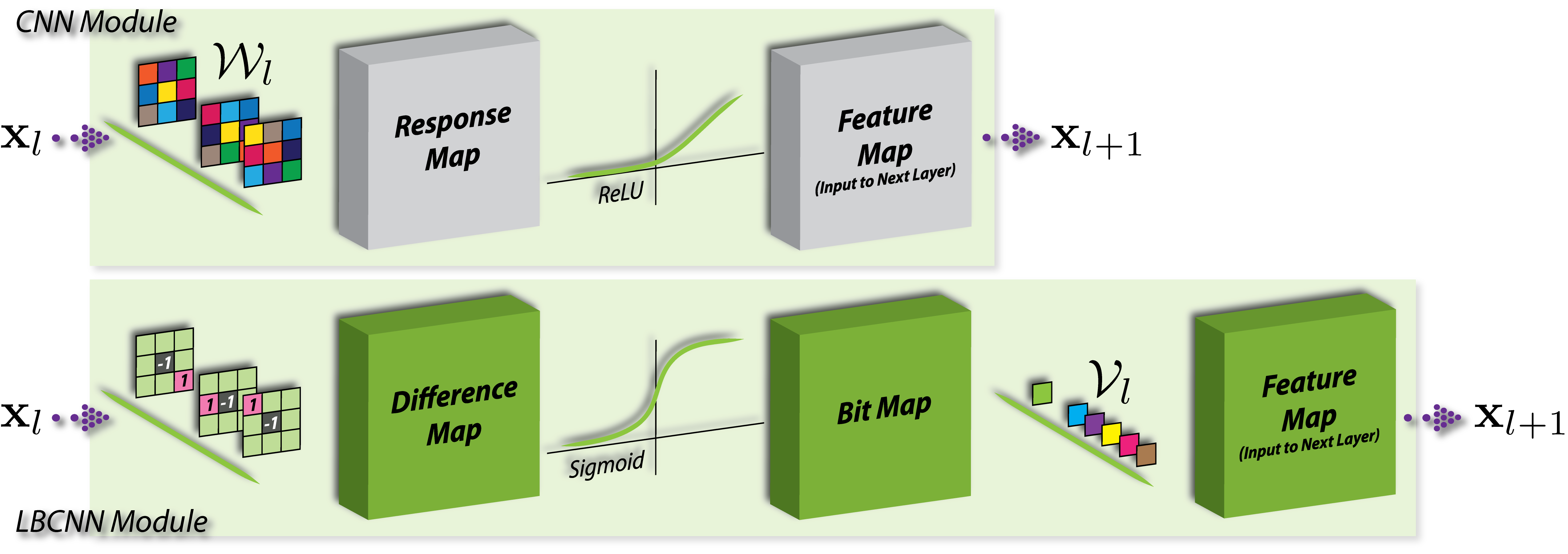
Our LBCNN module is designed to approximate a fully learnable dense CNN module.
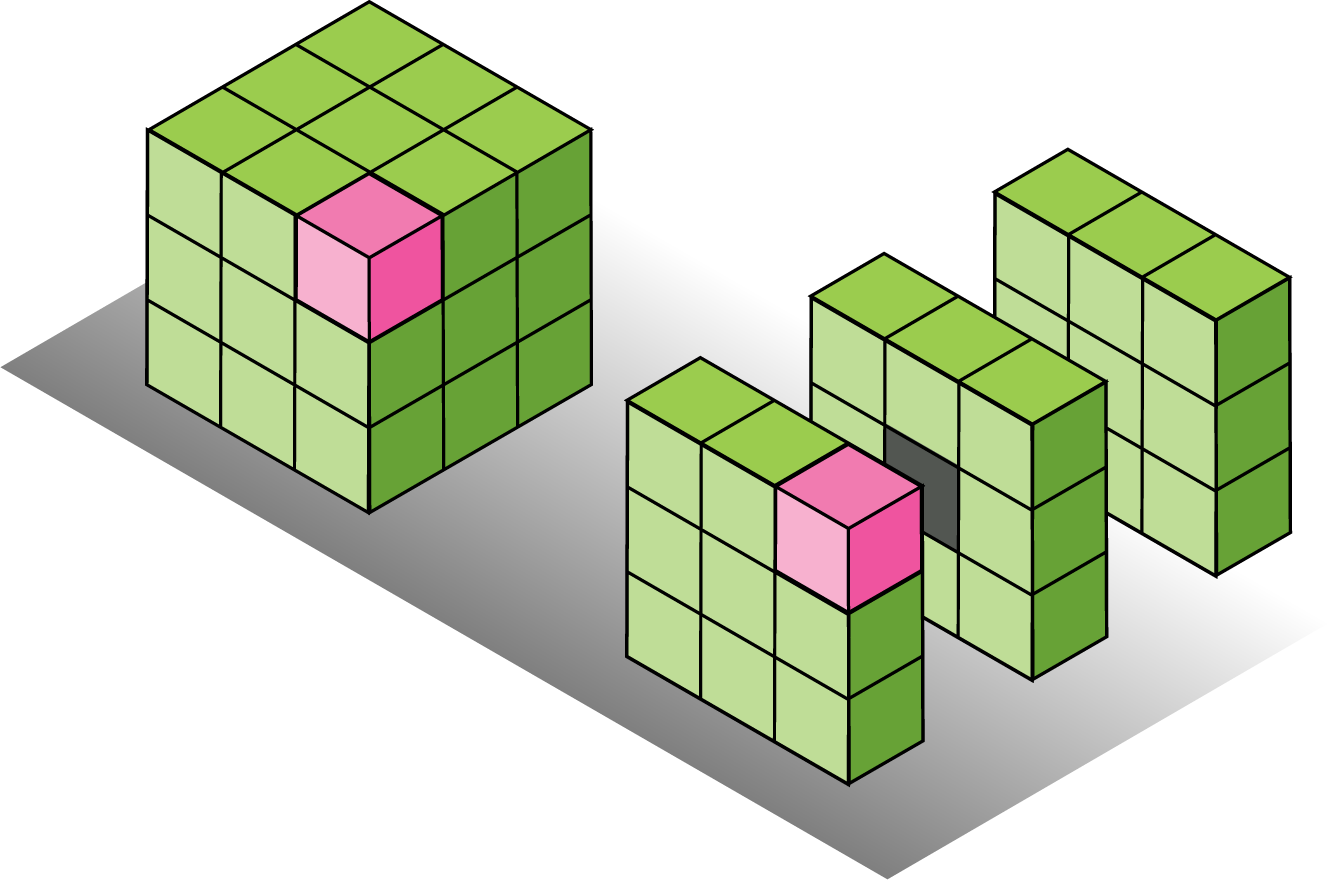
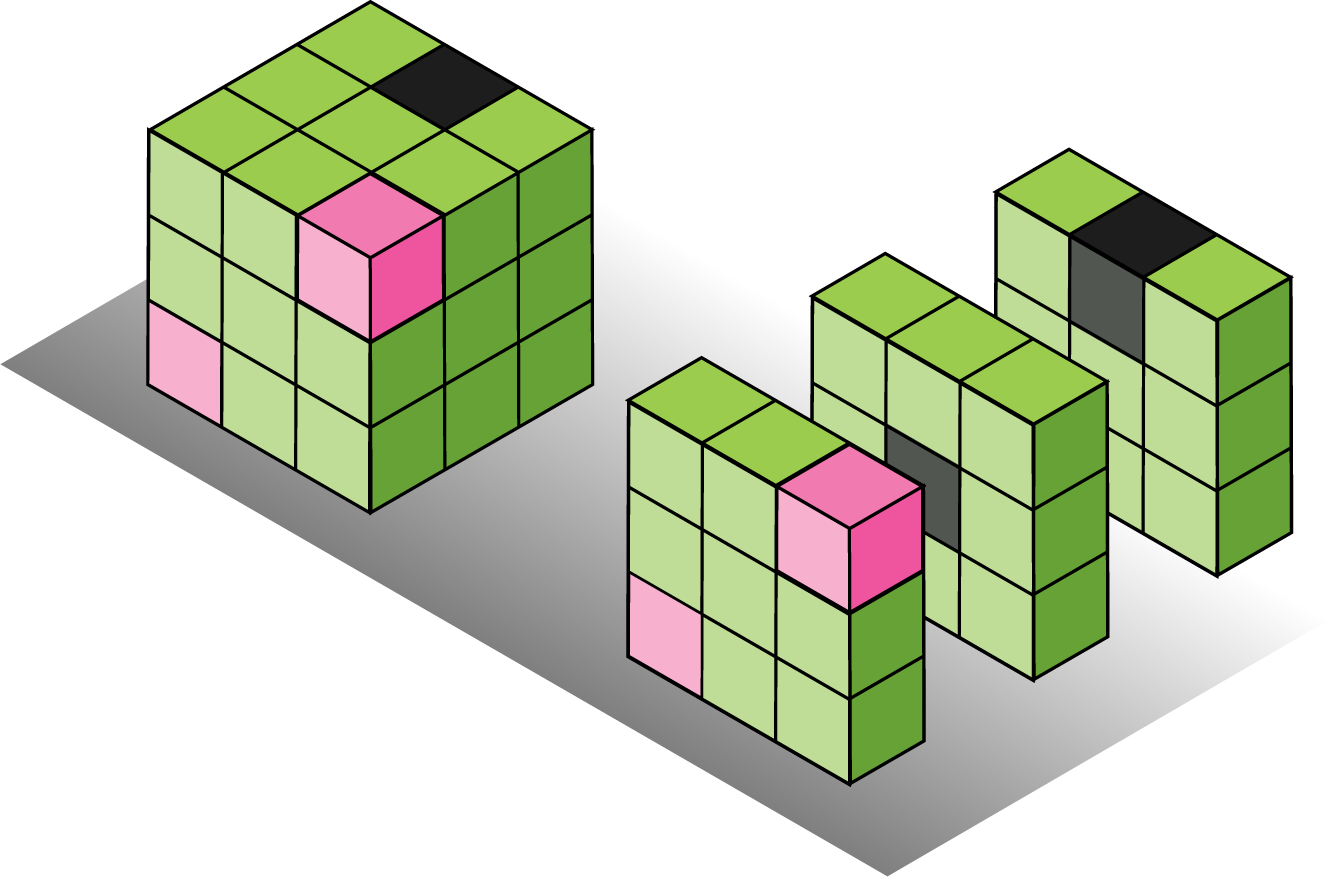
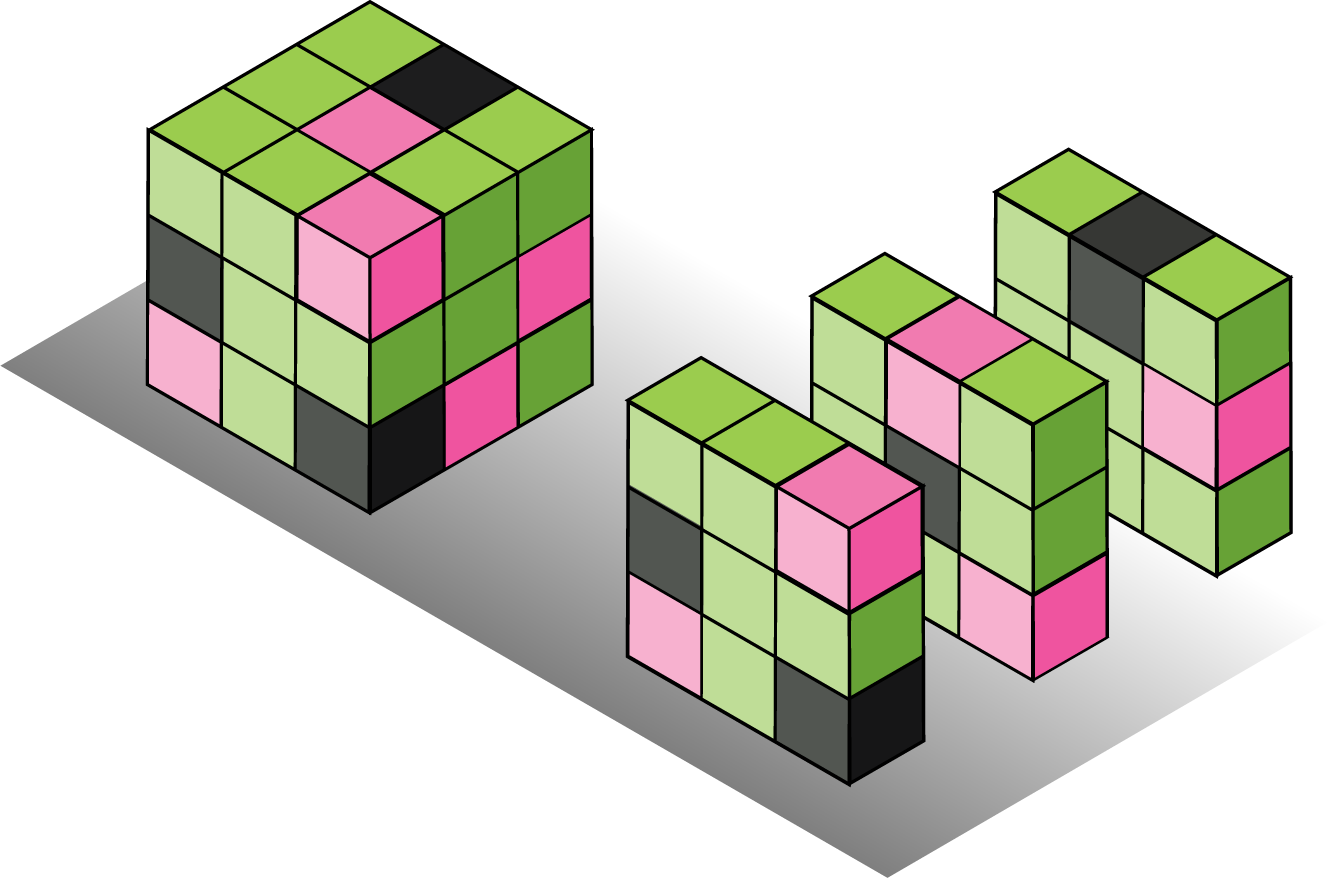
Binary convolutional kernels with different sparsity levels.
The proposed Local Binary Convolutional Neural Networks (LBCNN) aims at:
Statistical efficiency
Significant parameter savings: 9x to 169x in the number of learnable parameters.
Less prone to overfitting, converges faster, can learn from much fewer training samples.
Computation efficiency
Significant model size savings: 9x to 169x.
Significant computation savings: due to sparse binary convolutions.
On-par performance with standard CNNs (ImageNet, CIFAR-10, MNIST, SVHN)
To appear in IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017. (Spotlight Oral Presentation)
@inproceedings{juefei-xu2017lbcnn,
title={{Local Binary Convolutional Neural Networks}},
author={Felix Juefei-Xu and Vishnu Naresh Boddeti and Marios Savvides},
booktitle={IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month={July},
year={2017}
}